

This is a simulation of scattering from the COBRA cavity of a plane wave incident upon the cavity aperture, obtained by solving the time-harmonic Maxwell equations.
The problem is discretized with order 2 Nédélec edge finite elements, with 10 mesh points per wavelength.
The resulting indefinite linear system has 198 million degrees of freedom at frequency f = 16 GHz.
The problem is solved in parallel by a two-level Schwarz domain decomposition method, with a total computing time of 363 seconds on 6144 cores.
This is a direct acoustic simulation with the SEG/EAGE Overthrust seismic model, obtained by solving the Helmholtz equation.
The problem is discretized with P2 Lagrange finite elements, with 5 mesh points per wavelength.
The mesh is adapted to the spatial variations of the velocity to obtain a constant number of points per wavelength in the whole domain to save computation time.
The resulting indefinite linear system has 678 million degrees of freedom at frequency f = 20 Hz.
The problem is solved in parallel by a Schwarz domain decomposition method, with a total computing time of 218 seconds on 12288 cores.
This is a medical application of microwave tomographic imaging of cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs), also called brain strokes. This work has been carried out within the ANR project MEDIMAX and in collaboration with EMTensor GmbH, Vienna (Austria), an electromagnetic medical imaging company.
It has been awarded the Bull-Joseph Fourier 1st Prize 2015 and demonstrates on synthetic data the feasibility of a new microwave imaging technique allowing for the characterization of CVAs (ischemic or hemorrhagic), beginning with the very first instance of patient care in an ambulance and extending to continuous patient monitoring during hospitalization.
EMTensor’s experimental system consists of an electromagnetic reverberating chamber surrounded by five layers of 32 antennas each.
The inversion algorithm reconstructs an image of the head from the measurements (the 160x160 scattering matrix), corresponding to a map of the dielectric properties of the different head tissues.
The inversion is done using a L-BFGS algorithm, which involves repeatedly solving the direct problem modeled by Maxwell equations in the chamber, with a complex and highly heterogeneous medium.
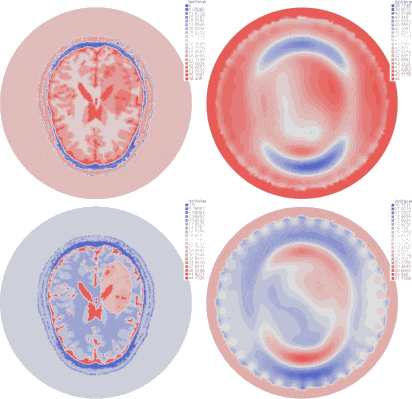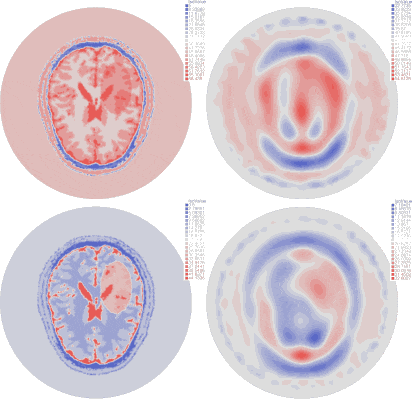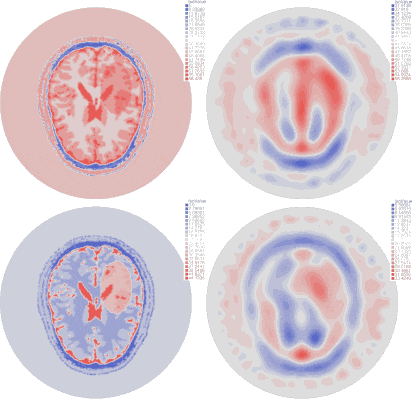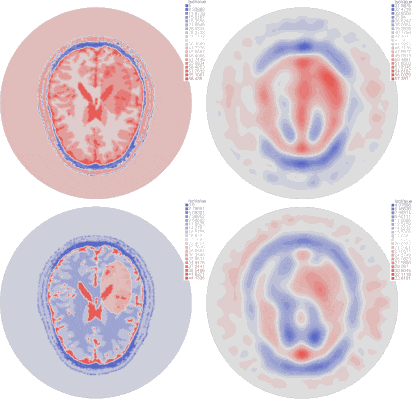
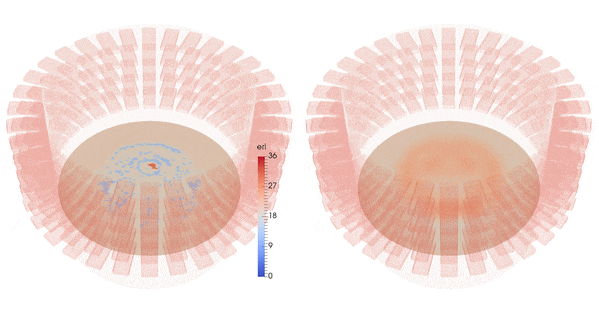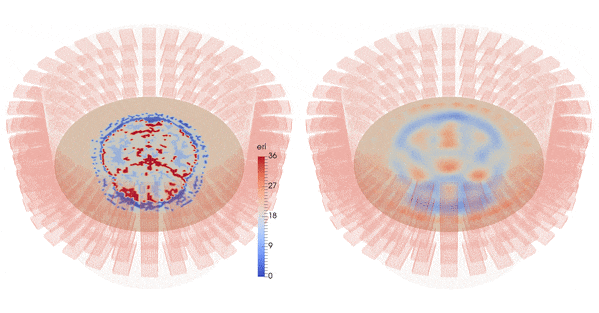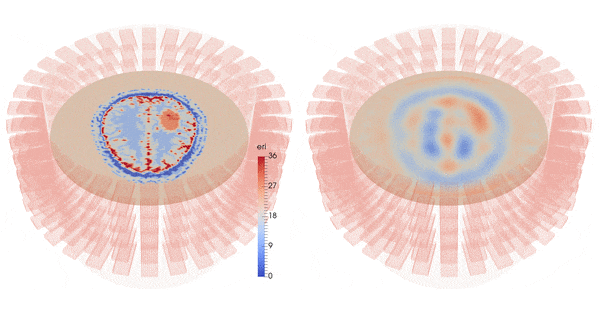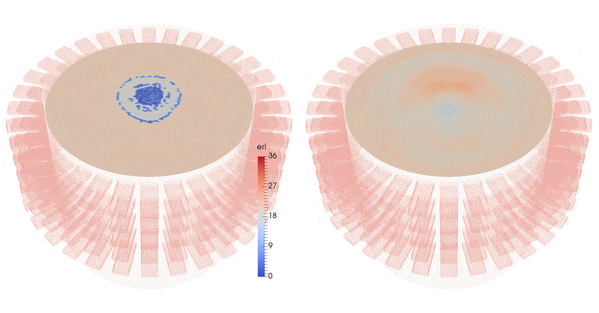
Results are obtained using synthetic data corresponding to a very precise numerical brain model from EMTensor with a simulated hemorrhagic stroke.
We add 10% Gaussian white noise to the data.
We can create parallelism by reconstructing the image in successive slices and solving five smaller inverse problems independently, each problem corresponding to one ring of antennas.
This, together with the parallelism coming from the domain decomposition method as well as solving for multiple right-hand sides, allows us to reconstruct an image corresponding to one ring in less than two minutes (94 seconds) using 4096 computing cores.
In the context of the development of sustainable agriculture aiming at preserving natural resources and ecosystems, it is necessary to improve our understanding of underground processes and interactions between soil and plant roots. Although the root system is responsible for taking up water and nutrients from the surrounding soil, roots are hidden below ground and measurements are difficult to obtain.
In this work, mechanistic models and numerical tools were developed for the simulation of soil water and solute transport with plant root uptake at the whole root system scale while taking the three-dimensional architecture of the root system explicitly into account. An emphasis is put on resolving the geometry of the root system as well as small-scale processes occurring in the rhizosphere, which play a major role in plant root uptake. The models are governed by nonlinear parabolic equations and can be used to study how the uptake pattern is affected by the shape and architecture of the root system.
In order to make these large 3D numerical simulations tractable, we take advantage of unstructured mesh adaptation and parallel computing tools available in FreeFEM. The mesh adaptation procedure allows to accurately represent the geometry of the root system in the soil domain and capture the high gradients expected near the roots. The most accurate model relies on an implicit representation of the actual surface of the roots through a level set approach, splitting the computational domain between the soil domain and the root system. Soil and root water flow are then coupled and solved in a monolithic way. Some numerical simulations of water uptake by maize root systems are shown here.
| Numerical head immersed in the imaging chamber, with a simulated ellipsoid-shaped hemorrhagic stroke |
|---|
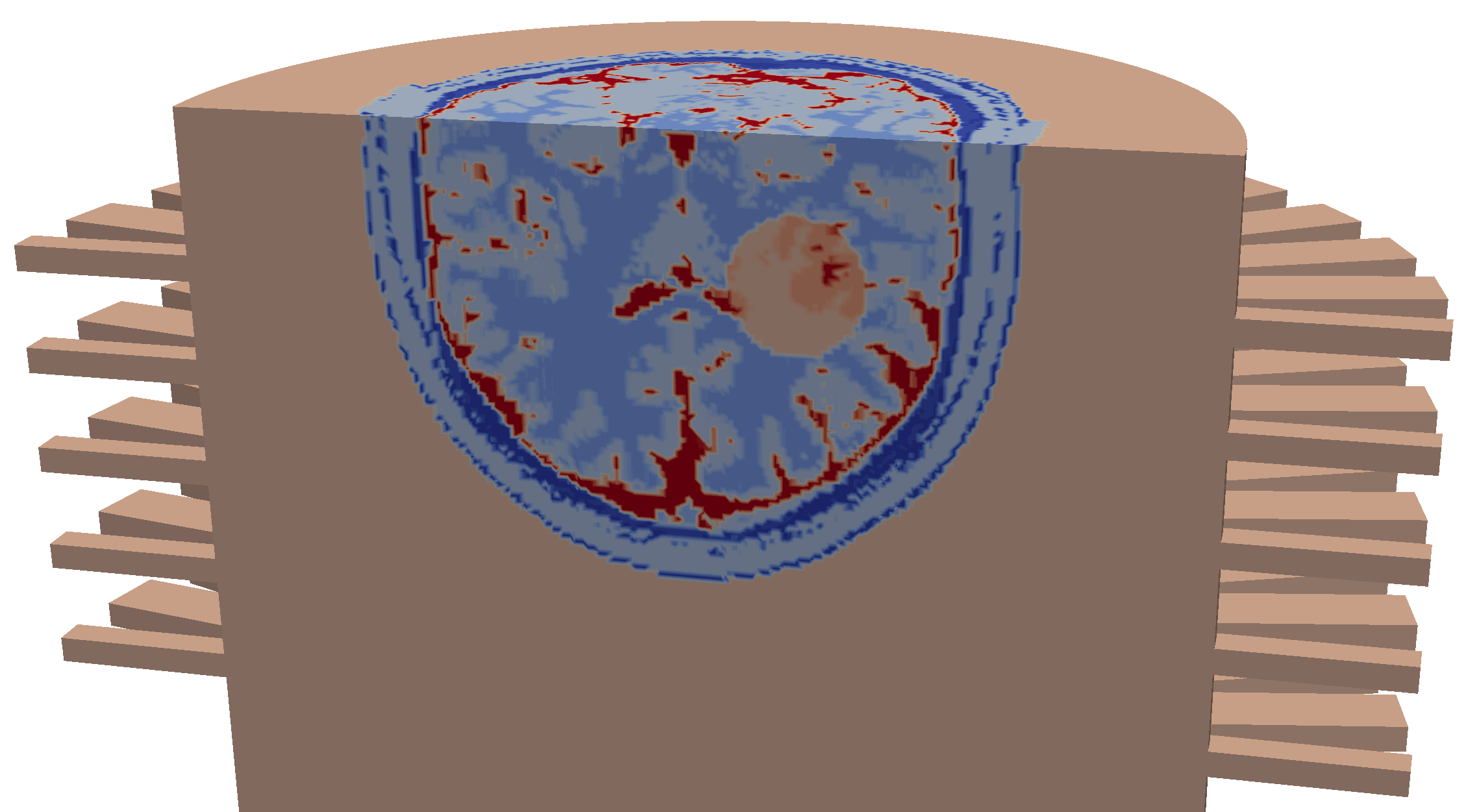 |
| Computational domain corresponding to the EMTensor imaging system prototype |
|---|
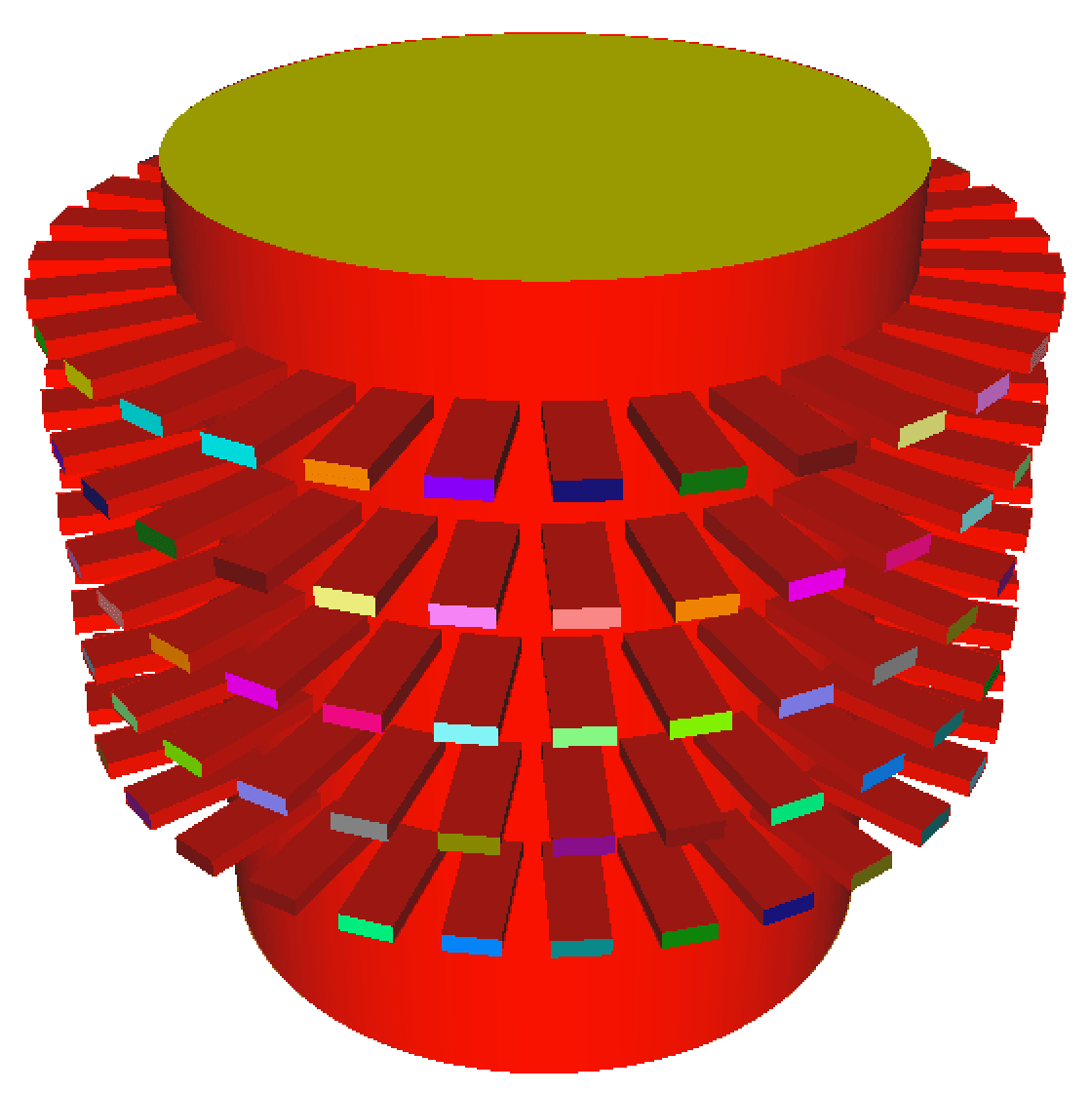 |
| Imaginary part of the reconstructed permittivity obtained by solving the inverse problem for the top layer with three different synthetic data sets (bottom row), created from a numerical brain model with three steps of the stroke evolution (healthy, small stroke, large stroke) with 10% white Gaussian noise (top row) |
|---|
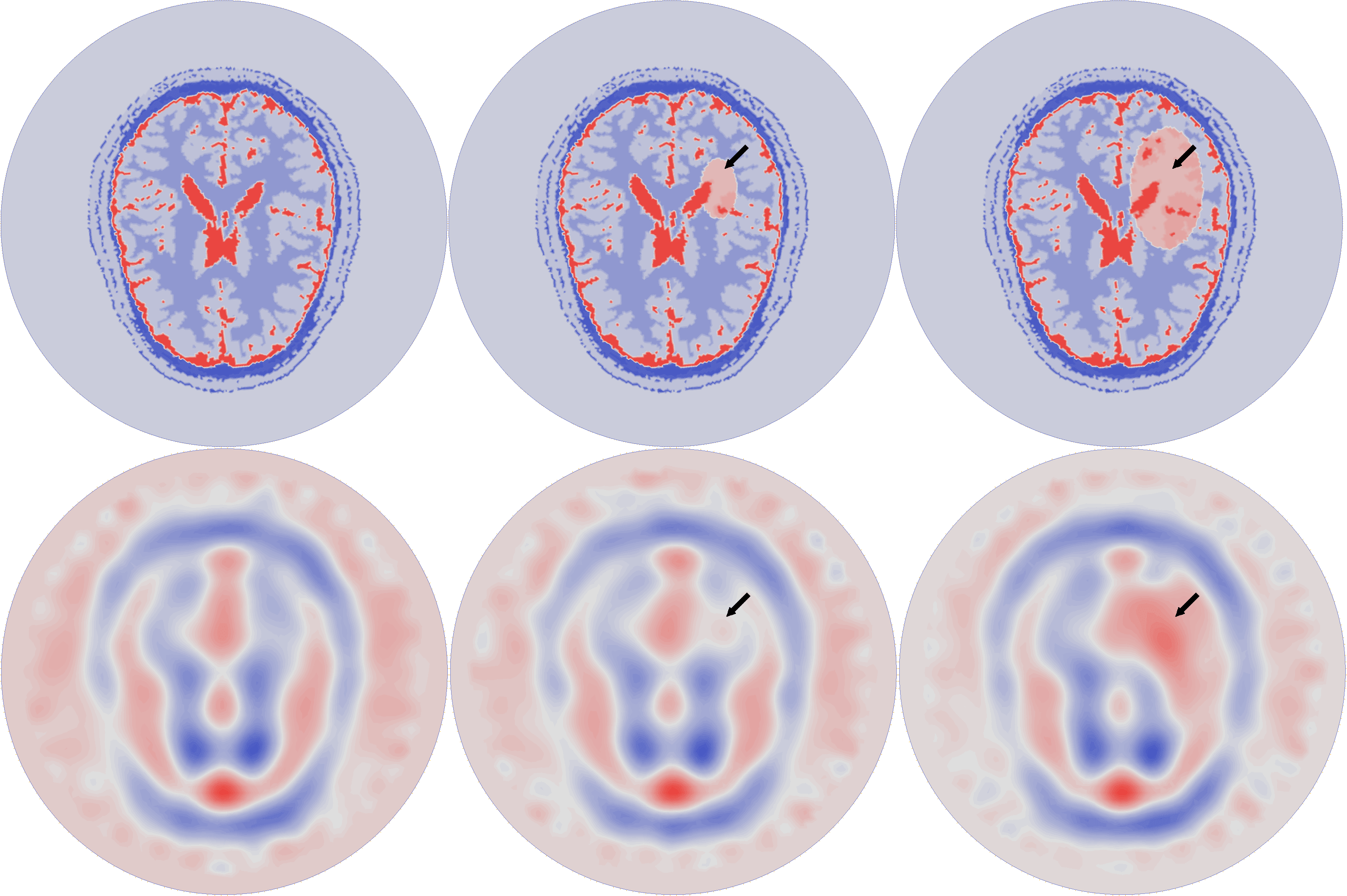 |
| Real (top row) and imaginary (bottom row) part of the reconstructed permittivity during 30 BFGS iterations (right column) using synthetic data created from a numerical brain model with hemorrhagic stroke (left column) with 10% white Gaussian noise |
|---|
 |
| Imaginary part of the reconstructed permittivity in the whole chamber (right) from synthetic data created from a numerical brain model with hemorrhagic stroke (left) with 10% white Gaussian noise |
|---|
 |